The stock market is a platform where individuals and institutions can buy and sell shares of publicly traded companies. Stocks represent ownership in a company and provide investors with an opportunity to participate in the growth and profitability of businesses. Investing in stocks can be an excellent way to build wealth and achieve financial goals, but it requires understanding the basics and making informed decisions. In this blog, we will delve into the world of stocks in India and explore how you can invest in them.
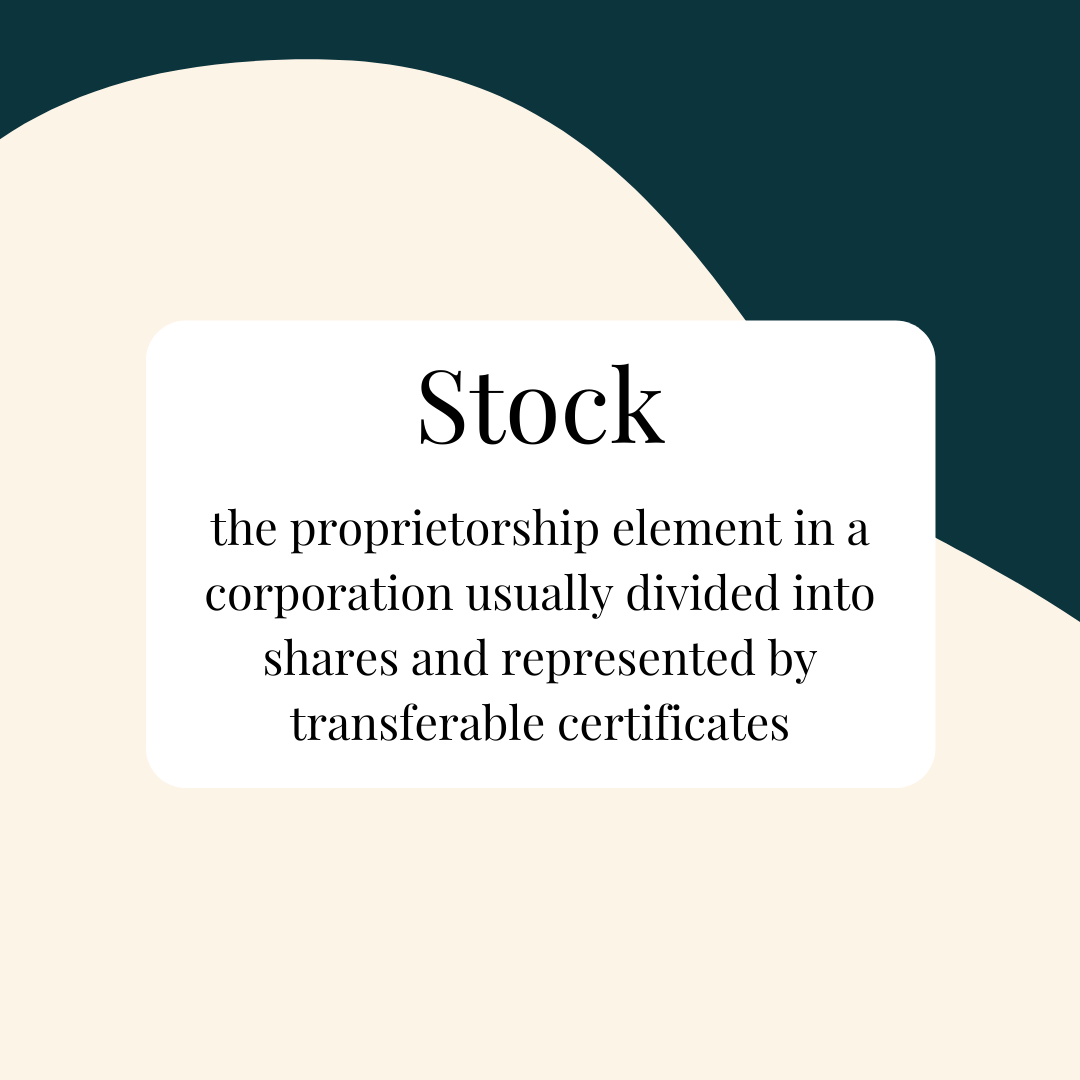
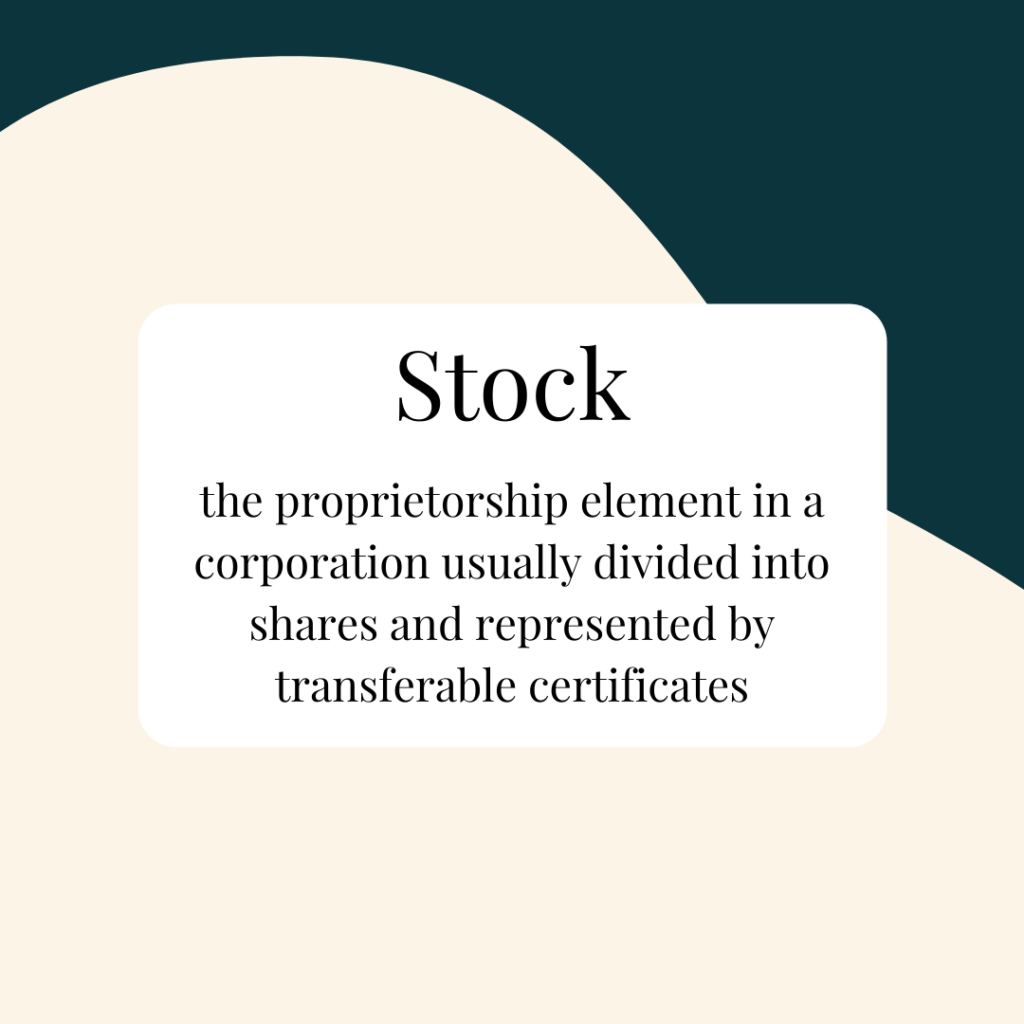
What are Stocks?
Stocks, also known as shares or equities, represent ownership in a company. When you buy stocks, you become a shareholder and have a claim on the company’s assets and earnings. Stocks are typically issued by publicly traded companies that have decided to raise capital by selling ownership stakes to the public.
Ownership in a company is divided into shares, and each share represents a portion of the company’s overall ownership. For example, if a company has issued one million shares and you own 1,000 shares, you would own 0.1% of the company. The value of your shares will fluctuate based on various factors, including the company’s performance, market conditions, and investor sentiment.
Stocks provide investors with several potential benefits:
- Potential for Capital Appreciation: As a shareholder, you have the opportunity to benefit from the company’s growth and profitability. If the company performs well, the value of its stock may increase over time, allowing you to sell your shares at a higher price and realize a capital gain.
- Dividend Income: Some companies distribute a portion of their earnings to shareholders in the form of dividends. Dividends are usually paid in cash or additional shares and provide a regular income stream to investors.
- Voting Rights: Common stockholders typically have the right to vote on certain company matters, such as electing the board of directors or approving significant corporate decisions. This allows shareholders to have a say in the company’s direction.
- Portfolio Diversification: Stocks offer the opportunity to diversify your investment portfolio by investing in different companies across various industries and sectors. Diversification helps spread the risk and potentially minimize the impact of any individual stock’s performance on your overall portfolio.
Investing in stocks involves risks, and the value of stocks can fluctuate widely. It is important to thoroughly research companies before investing and to understand the potential risks and rewards associated with stock market investing. Many investors choose to consult financial advisors or conduct their own analysis to make informed investment decisions.
How does Stock Market Work?
The stock market in India operates similarly to stock markets in other countries. Here’s an overview of how the stock market works in India:
- Stock Exchanges: The two primary stock exchanges in India are the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and the National Stock Exchange (NSE). These exchanges provide a platform for trading stocks and other financial instruments. The BSE, established in 1875, is the oldest stock exchange in Asia, while the NSE, founded in 1992, is the largest stock exchange in India in terms of trading volume.
- Listing and Initial Public Offering (IPO): Companies in India can list their shares on the stock exchanges through an IPO. Before listing, companies work with investment banks and underwriters to determine the offer price and issue shares to the public. The IPO process involves filing a prospectus with regulatory authorities, conducting roadshows, and offering shares to institutional and retail investors.
- Trading Mechanism: In India, stock trading occurs electronically through a system called the Electronic Trading System (ETS) or Trading Terminal. Investors can trade stocks through brokers or online trading platforms that are registered with the stock exchanges.
The trading day in India is divided into several sessions:
- Pre-opening Session: This session allows investors to place orders to buy or sell stocks before the market opens. It consists of three phases: the pre-open order collection, order matching, and the post-closing session.
- Continuous Trading Session: The primary trading session where buyers and sellers place orders, and trades are executed based on the prevailing market prices. The continuous trading session is further divided into several periods.
- Closing Session: This session allows for the calculation of closing prices and the determination of the closing price index.
- Market Participants: The stock market in India involves various participants, including individual investors, institutional investors, brokers, market makers, and regulatory bodies. The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) is the regulatory authority responsible for overseeing the securities market in the country.
- Indices: The stock market in India has several indices that track the performance of stocks. The two most widely followed indices are the BSE Sensex and the Nifty 50. The Sensex represents the performance of 30 stocks listed on the BSE, while the Nifty 50 represents the performance of 50 stocks listed on the NSE. These indices serve as indicators of the overall market performance.
- Market Regulations: SEBI plays a crucial role in regulating the stock market in India. It formulates rules and regulations, monitors market activities, and protects the interests of investors. SEBI ensures transparency, fair practices, and investor protection in the securities market.
Investors in the Indian stock market need to open a Demat (Dematerialized) account and a trading account with a registered broker to participate in trading. They can place orders to buy or sell stocks based on their investment strategies and goals.
It’s important to note that investing in the stock market involves risks, and investors should carefully analyze companies, consider their financial goals and risk tolerance, and diversify their portfolios to mitigate risks.
Steps to Invest in Stocks in India
Investing in the stock market in India can be a rewarding way to grow wealth over the long term. Here are the general steps to get started with investing in the Indian stock market:
- Set Investment Goals: Determine your financial goals and objectives. Are you investing for retirement, a specific purchase, or long-term wealth creation? Setting clear goals will help you determine your investment strategy and time horizon.
- Research and Educate Yourself: Before investing, it’s essential to educate yourself about the stock market and understand the basics of investing. Learn about different investment instruments, investment strategies, and risk management techniques. Read books, attend seminars, and explore reputable online resources to enhance your knowledge.
- Determine your Risk Tolerance: Assess your risk tolerance level, which refers to your ability and willingness to take on risk. Consider your financial situation, investment goals, time horizon, and personal comfort with fluctuations in the stock market. This will help you select appropriate investment options that align with your risk tolerance.
- Open a Demat and Trading Account: To invest in the Indian stock market, you need to open a Demat (Dematerialized) account and a trading account. A Demat account holds your shares in electronic form, and a trading account enables you to buy and sell shares. You can open these accounts with a registered stockbroker or a financial institution.
- Choose a Reliable Stockbroker: Select a reputable and reliable stockbroker that suits your needs. Consider factors such as brokerage fees, customer service, trading platforms, research and analysis tools, and the ease of account management. Many brokers now offer online trading platforms that provide convenience and accessibility.
- Determine Your Investment Strategy: Decide on an investment strategy based on your investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Common strategies include long-term investing, value investing, growth investing, or a combination of different approaches. Your strategy will guide your stock selection and trading decisions.
- Research Companies: Conduct thorough research on companies before investing in their stocks. Analyze their financial statements, earnings reports, industry position, competitive advantages, and future growth prospects. Consider factors such as revenue growth, profitability, management quality, and sustainability. Pay attention to the company’s industry and economic factors that may impact its performance.
- Diversify Your Portfolio: Diversification is key to managing risk. Spread your investments across different sectors, industries, and companies to reduce exposure to individual stock volatility. Avoid putting all your capital into a single stock or sector. A diversified portfolio helps mitigate risk and can potentially enhance returns.
- Start with a Small Investment: Begin with a small investment to gain experience and confidence. Consider investing in mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) as they offer diversification and professional management. As you become more comfortable and knowledgeable, you can gradually increase your investment.
- Monitor and Review Your Portfolio: Regularly monitor your portfolio and stay updated with company news, market trends, and economic developments. Review your investments periodically to ensure they align with your goals and make adjustments if necessary. Avoid making impulsive decisions based on short-term market fluctuations.
- Stay Informed: Stay informed about market trends, economic indicators, and company-specific news. Follow reliable financial news sources, read annual reports, and keep track of analyst recommendations. This information can help you make informed investment decisions.
- Stay Disciplined: Investing in the stock market requires discipline and a long-term perspective. Avoid making emotional decisions based on short-term market fluctuations. Stick to your investment strategy and be patient with your investments. Over time, disciplined investing can yield favorable results.
Remember, investing in the stock market involves risks, and past performance is not indicative of future results. It’s advisable to consult with a financial advisor or a professional before making any investment decisions.
Conclusion
Investing in stocks in India can be a rewarding way to grow your wealth, but it requires careful consideration and a long-term perspective. By educating yourself, setting investment goals, choosing the right broker, conducting thorough research, and creating a diversified portfolio, you can enhance your chances of making successful investments.