Mutual funds have gained significant popularity as an investment option in India. Whether you are a seasoned investor or a beginner looking to grow your wealth, mutual funds provide a diversified and professionally managed approach to investing. In this blog, we will explore what mutual funds are and discuss the steps to invest in mutual funds in India.

What is a Mutual Fund?
A mutual fund is an investment vehicle that pools money from multiple investors and invests it in a diversified portfolio of securities. The pool of funds collected from investors is managed by professional fund managers or investment companies, who make investment decisions on behalf of the investors.
The main objective of a mutual fund is to provide investors with an opportunity to invest in a wide range of assets, such as stocks, bonds, money market instruments, and other securities, without requiring them to directly buy and manage individual securities themselves. By pooling funds together, investors can benefit from economies of scale, professional expertise, and diversification.
Diversification is a key advantage of mutual funds. Since mutual funds invest in a variety of securities, they spread the investment risk across multiple assets. This helps to reduce the impact of poor performance of any single security on the overall portfolio. It also allows investors with limited capital to gain exposure to a diversified investment portfolio.
Mutual funds are managed by professional fund managers who conduct research and analysis to identify investment opportunities and make investment decisions. These managers have the expertise and experience to select securities based on the fund’s investment objective, whether it is capital appreciation, income generation, or a combination of both. They constantly monitor the performance of the portfolio and make adjustments as needed.
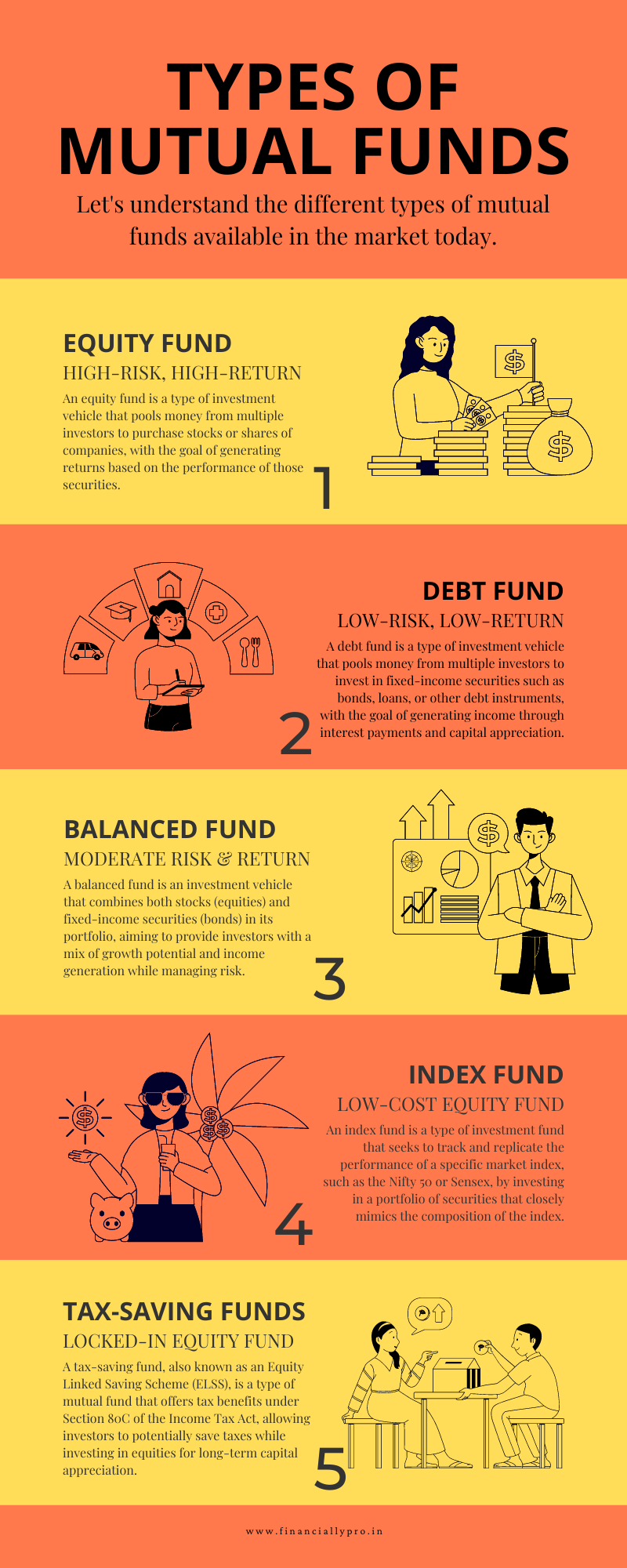
There are various types of mutual funds available to cater to different investment objectives and risk appetites. As mentioned earlier, equity funds primarily invest in stocks, debt funds invest in fixed-income instruments, balanced funds provide a mix of equities and debt, index funds aim to replicate market indices, sector funds focus on specific sectors, and tax-saving funds offer tax benefits while investing in equities.
Investing in mutual funds offers several advantages. Firstly, mutual funds provide access to professional investment management even for small investors. Secondly, they offer liquidity, allowing investors to buy or sell their fund units at the prevailing Net Asset Value (NAV) on any business day. Moreover, mutual funds provide transparency, as they are required to disclose their portfolio holdings and performance regularly.
To invest in mutual funds in India, investors need to complete the KYC (Know Your Customer) process, which involves submitting necessary documents to comply with regulatory requirements. Once the KYC process is completed, investors can choose the mode of investment, such as investing directly through a mutual fund company, using online platforms, or seeking assistance from intermediaries like banks or financial advisors. Investors can opt for lump sum investments or set up a Systematic Investment Plan (SIP) to invest a fixed amount at regular intervals.
Types of Mutual Funds
Mutual funds come in various types, each designed to cater to different investment objectives, risk profiles, and time horizons. Let’s explore some of the common types of mutual funds:
- Equity Funds: Equity funds primarily invest in stocks of companies across different sectors and market capitalizations. These funds aim for long-term capital appreciation by taking advantage of the growth potential of the stock market. Equity funds can be further classified based on market capitalization, such as large-cap funds (investing in large, well-established companies), mid-cap funds (investing in medium-sized companies), and small-cap funds (investing in small, emerging companies). These funds carry a higher level of risk but also offer the potential for higher returns over the long term.
- Debt Funds: Debt funds invest in fixed-income securities like government bonds, corporate bonds, debentures, and money market instruments. These funds aim to provide stable income and relatively lower risk compared to equity funds. Debt funds can be further classified based on the duration of the underlying securities, such as liquid funds (short-term investments with high liquidity), short-term funds, medium-term funds, and long-term funds. Investors looking for regular income or capital preservation often consider debt funds.
- Balanced Funds: Also known as hybrid funds, balanced funds invest in a mix of equities and debt instruments. These funds aim to provide a balance between capital appreciation and regular income. Balanced funds are suitable for investors seeking moderate risk and who prefer a diversified portfolio comprising both stocks and fixed-income securities. The allocation between equities and debt may vary based on the fund’s investment objective and market conditions.
- Index Funds: Index funds aim to replicate the performance of a specific market index, such as the Nifty 50 or Sensex. These funds passively manage their portfolios by investing in the same securities and in the same proportion as the underlying index. Index funds offer broad market exposure and are a popular choice for investors seeking low-cost investment options. They generally have lower expense ratios compared to actively managed funds.
- Sector Funds: Sector funds focus on specific sectors or industries, such as technology, healthcare, banking, energy, or real estate. These funds invest predominantly in companies operating within the chosen sector. Sector funds carry a higher level of risk as their performance is closely tied to the performance of the specific sector. They are suitable for investors who have a strong belief in the growth potential of a particular sector.
- Tax-saving Funds (ELSS): Equity Linked Savings Schemes (ELSS) are tax-saving mutual funds that offer tax benefits under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act in India. ELSS funds have a lock-in period of three years, and investments in these funds are eligible for a deduction of up to Rs. 1.5 lakhs from taxable income. ELSS funds invest predominantly in equities and offer the potential for long-term capital appreciation along with tax benefits.
- International Funds: International or global funds invest in securities of companies listed outside of India. These funds provide exposure to global markets and allow investors to diversify their portfolios geographically. International funds can focus on specific regions like the US, Europe, or emerging markets. Investing in international funds can provide opportunities to benefit from global economic growth and diversify risk across different countries.
How to invest in Mutual Funds?
Investing in mutual funds in India involves a few key steps. Here’s a detailed guide on how to invest in mutual funds:
- Set your Investment Goals: Define your investment objectives, whether it is long-term wealth creation, funding a specific goal like education or retirement, or generating regular income. Understanding your financial goals will help you choose the appropriate mutual funds.
- Research and Selection: Conduct thorough research on different mutual fund schemes available in the market. Consider factors such as the fund’s investment objective, past performance, fund manager’s track record, expense ratio, risk profile, and investment philosophy. Financial websites, fund house websites, and expert advice can provide valuable insights for making an informed decision.
- Complete KYC Compliance: Before investing in mutual funds, complete the KYC (Know Your Customer) process. Submit the necessary documents, such as identity proof (PAN card), address proof, and a recent passport-size photograph, to comply with regulatory requirements. You can fulfill the KYC process by visiting a mutual fund office, registrar office, or using online platforms facilitating KYC compliance.
- Choose the Mode of Investment: Decide how you want to invest in mutual funds. You have several options, including investing directly through the mutual fund company, using online platforms, or seeking assistance from intermediaries like banks or financial advisors. Online platforms offer convenience, ease of comparison, and the ability to track your investments.
- Select the Investment Method: Mutual funds provide two investment options: lump sum investment or Systematic Investment Plan (SIP). In a lump sum investment, you invest a significant amount at once. On the other hand, SIP allows you to invest a fixed amount at regular intervals (monthly, quarterly, etc.). SIPs offer the benefit of rupee-cost averaging, reducing the impact of market volatility on your investment.
- Fill the Application Form: Obtain the mutual fund application form either from the mutual fund company’s website, distributor platforms, or the mutual fund office. Fill in the required details, such as personal information, investment amount, scheme name, and payment method.
- Make Payment: Choose your preferred payment method for investing in mutual funds. You can pay through online banking, debit card, NEFT/RTGS, or electronic payment gateways. Some platforms also support payment through checks or demand drafts. Ensure that you provide accurate details and verify the payment process to avoid any errors.
- Provide Necessary Declarations: Along with the application form, you may need to provide additional declarations, such as nominee details and investment preferences (growth or dividend option). Ensure that you provide all the required information accurately.
- Review and Monitor your Investments: Once your investment is made, regularly review the performance of your mutual fund holdings. Keep track of the fund’s performance, any changes in the investment strategy, and market trends. Periodically reassess your investment goals and risk appetite to make any necessary adjustments to your portfolio.
Remember, investing in mutual funds involves market risks, and past performance is not indicative of future results. It is advisable to consult a financial advisor or professional for personalized advice based on your financial situation and investment goals. Regularly educate yourself about investment concepts and stay updated with market trends to make well-informed investment decisions.
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about mutual funds:
What are the benefits of investing in mutual funds?
- Diversification: Mutual funds allow you to invest in a diversified portfolio, reducing the risk associated with investing in individual securities.
- Professional Management: Experienced fund managers make investment decisions on behalf of investors, utilizing their expertise and research capabilities.
- Accessibility: Mutual funds are easily accessible, with various investment options and minimum investment requirements.
- Liquidity: Mutual funds offer liquidity, allowing investors to buy or sell their fund shares on any business day at the net asset value (NAV) price.
How do mutual funds make money?
Mutual funds make money through various means, such as expense ratios, sales charges (load funds), and management fees. Expense ratios cover the fund’s operating expenses, including administrative costs, management fees, and marketing expenses.
What is an expense ratio?
An expense ratio is the annual fee charged by a mutual fund to cover its operating expenses. It is expressed as a percentage of the fund’s average net assets. A lower expense ratio is generally more favorable for investors, as it reduces the impact on overall returns.
How can I track the performance of a mutual fund?
Mutual fund performance can be tracked through various means. Most fund providers and financial websites provide information on a fund’s historical performance, including returns over different time periods. You can also find information on a fund’s performance relative to its benchmark index.
Can I lose money in mutual funds?
Yes, investing in mutual funds carries risks, and there is the potential to lose money. The value of mutual fund shares fluctuates with changes in the underlying securities held by the fund. It’s important to carefully consider your investment goals and risk tolerance before investing.
Can I switch between different mutual funds?
Many mutual fund providers allow investors to switch their investments from one fund to another within the same fund family. This can be done by filling out the necessary forms or making the request through an online account.







